

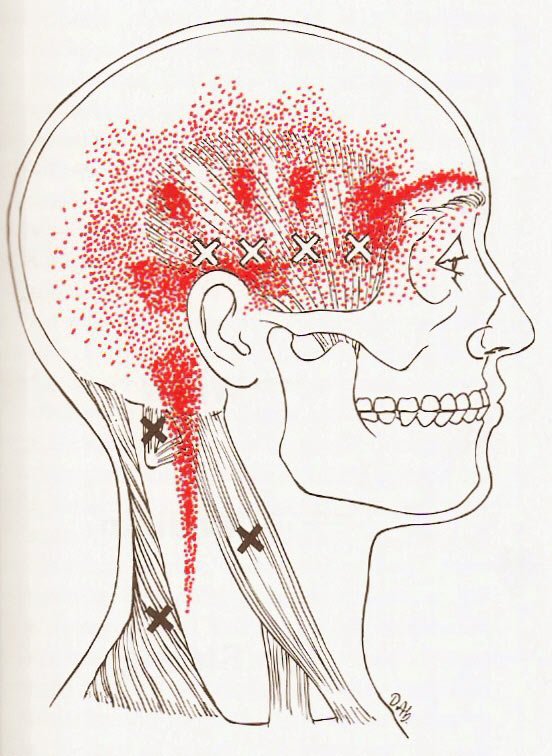
LTrPs pain can be triggered by digital compression, stretch, or overload. Latent Trigger Points (LTrPs) can be developed by maintaining a shortened muscle activation for a long period of time, exaggerated muscle contraction, or repeated physical activity. Two kinds of MTrPs are clinically described: latent and active. A MTrP is defined as a hypersensitive nodule located in skeletal muscles. The MTrPs are usually associated with (i) hyperalgesia, (ii) referred pain, (iii) behavioural perturbations, and (iv) functional limitations. Myofascial syndrome is a clinical condition characterized by muscle pain related to Myofascial Trigger Points (MTrPs). However, the MP of these patients is only partially improved after the IC application.

The results suggest the IC effectiveness on pain and MP impairment in subjects with LTrPs. However, one IC session did not allow the PG to get the same MP than the HG ( p < 0.05). Furthermore, the movement time (15.70 ± 2.05 p < 0.001) and the Fitts’ Law coefficient (0.80 ± 0.53 p < 0.001) were significantly reduced. After IC, the PG showed a significant decrease of pain (4.07 ± 1.91 p < 0.001). PG had a linear MP lower than the HG before treatment ( p < 0.05). Data were analysed with mixed factorial ANOVA for intergroup linear motor performance differences and dependent t-student test for intragroup pain differences. Subjective pain and linear MP (movement time and Fitts’ Law) were assessed before and after a linear tapping task. A quasiexperimental study was performed in twenty subjects allocated to either patients group with LTrPs (PG, n=10) or healthy group with no symptoms (HG, n=10). To analyse the effect of the manual ischemic compression (IC) on the upper limb motor performance (MP) in patients with LTrPs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
